With the latest release of VMware Cloud Foundation in version 9, VMware has introduced a few new concepts compared to VMware Cloud Foundation 5.2, in this blog post we will break down the new high-level architecture concepts and demystify the concepts of VCF Private Cloud, VCF Fleet, VCF Instances and VCF Domains as well as the related storage options.
VCF Private Cloud
The pinnacle of management and utilization of the core resources within a software-defined data center is encapsulated in the Virtual Cloud Foundation (VCF) private cloud architecture. This configuration may encompass one or multiple VCF fleets, thereby enhancing resource orchestration and scalability.

VCF Fleet
A single set of fleet-level management components governs the environment, specifically VCF Operations and VCF Automation. Within a VCF fleet, multiple VCF Instances can exist, and it may also include standalone vCenter instances, all of which are regulated by the VCF Operations instance associated with the fleet. Notably, the management domain of the initial VCF Instance within the VCF fleet serves as the host for the fleet-level management components.
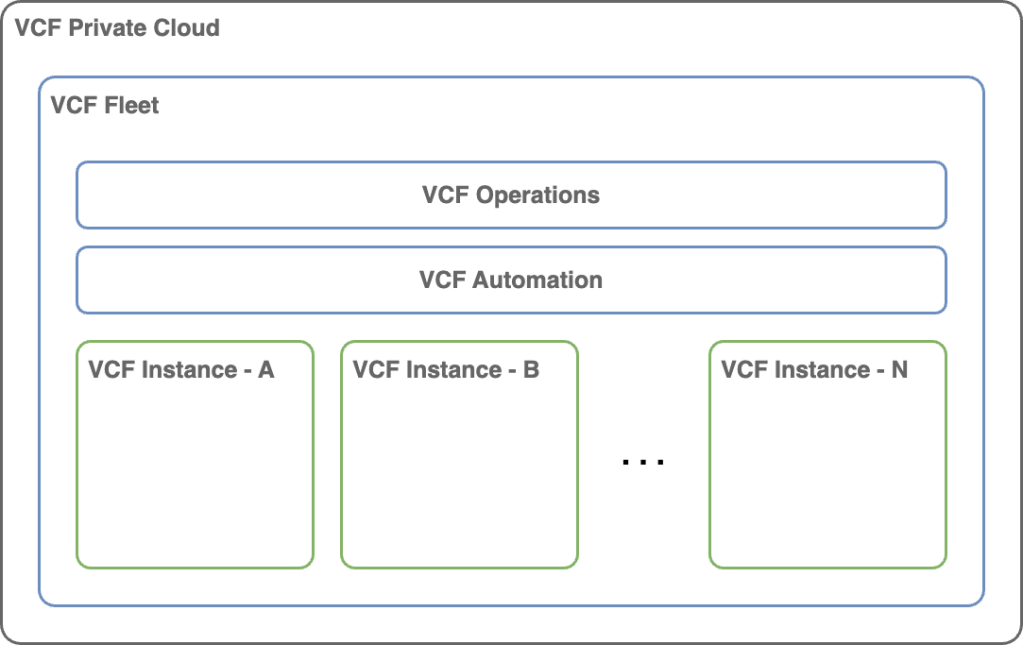
As a result of this VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) design concept is is also possible to operate multiple VCF Fleets within a VCF Private Cloud, each with its own VCF Operations and VCF Automation instances for strict separation and to meet compliance requirements.
VCF Instance
Virtual infrastructure comprising compute, storage, and networking resources is essential for executing business workloads. A VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) instance is partitioned into VCF domains, which include a management domain and optionally one or more workload domains. The initial vSphere cluster within the management domain is responsible for hosting the management components associated with the VCF instance.

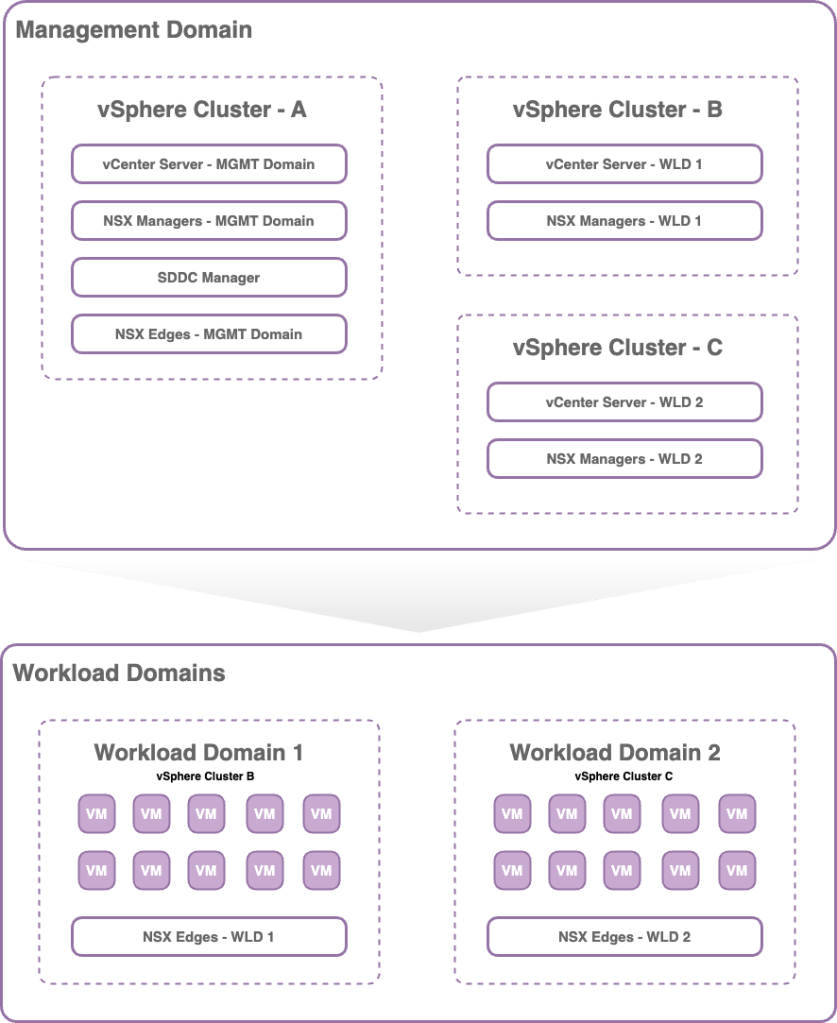
VCF Domain
A VCF Domain is a critical architectural component of a VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) instance, designed to delineate infrastructure into separate operational environments. This includes the management domain, which is responsible for executing core VCF management functionalities, and multiple workload domains that facilitate the deployment of virtual machines and containerized applications. These domains ensure the segregation of compute, storage, and networking resources, enabling distinct teams or applications to operate in isolation. By doing so, they support consistent management practices, enhance security protocols, and streamline patch management within a hybrid cloud environment.
Management Domain
The management domain is established during the deployment or convergence phase by the VCF Installer. It encompasses the core management components of the VCF Instance, and specifically for the initial VCF Instance, it integrates VCF Operations and VCF Automation.
Alongside the standard components present in each VCF domain, the management domain is distinguished by the inclusion of the SDDC Manager appliance and the fleet management appliance. These components enhance the VCF Operations instance by introducing workflows designed for automated infrastructure management within the VCF fleet.
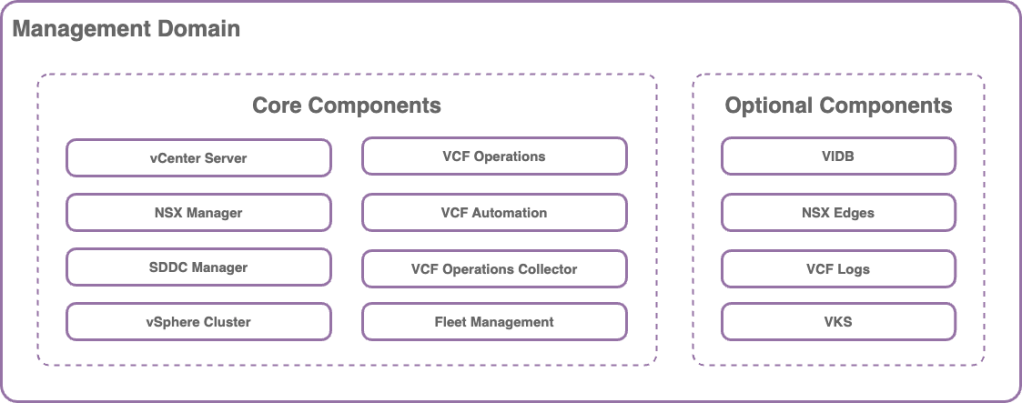
In VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9, there are two deployment types for VCF Domains, Simple Deployment and High Availability Deployment that have different hardware requirements and provide different levels of availability and redundancy for the management resources.
Simple Deployment
7 required appliances
- VCF Operations (1x)
- VCF Operations Collector (1x)
- VCF Automation (1x)
- vCenter Server (1x)
- SDDC Manager (1x)
- NSX Manager (1x)
- Fleet Management (1x)
7 optional appliances
- VIDB (3x)
- NSX Edge (2x)
- VCF Logs (1x)
- VKS (1x)
High Availability Deployment
13 required appliances
- VCF Operations (3x)
- VCF Operations Collector (1x)
- VCF Automation (3x)
- vCenter Server (1x)
- SDDC Manager (1x)
- NSX Manager (3x)
- Fleet Management (1x)
11 optional appliances
- VIDB (3x)
- NSX Edge (2x)
- VCF Logs (3x)
- VKS (3x)
Workload Domain
Creating workload domains within VCF Operations is essential for managing consumer workloads effectively. The inaugural workload domain established in your environment prompts VCF Operations to deploy a vCenter instance alongside an NSX Manager instance within the management domain. For each subsequent workload domain, an additional vCenter instance is provisioned. It is important to note that new workload domains can either utilize the same NSX Manager cluster shared with an existing workload domain or you have the option to deploy a new NSX Manager cluster. However, it is imperative to understand that workload domains are not permitted to access the NSX Manager cluster designated for the management domain.
Storage Options
VCF 9 introduces a range of advanced storage solutions, including vSAN HCI (Hyper-Converged Infrastructure), traditional NFS, VMFS, and Fibre Channel. These storage options are applicable for the initial management domain and can be seamlessly integrated within the same VCF instance across various workload domains. Additionally, VCF 9 enhances its functionality with new features such as sophisticated monitoring dashboards for vSAN, improved global deduplication capabilities, and expanded support for larger VMDKs and container storage.
Principal Storage – Management Domain
- vSAN HCI (ESA/OSA)
- NFS
- FC
Principal Storage – Workload Domain
- vSAN HCI (ESA/OSA)
- vSAN HCI (Storage Clusters)
- vSAN (Remote Datastores)
- NFS
- FC
Supplemental Storage – Add Capacity to any domain
- vSAN HCI (Storage Clusters)
- vSAN (Remote Datastores)
- NFS
- FC
- iSCSI
- NVMe (FC)
- NVMe (TCP)
Note:
Virtual Volumes (vVols) are officially classified as obsolete in VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9.0 and will be completely removed in the following version 9.1. The decision by Broadcom, the company behind VMware, means that vVols will only be usable to a limited extent in VCF 9.0 and will no longer be actively supported.

Leave a comment